New article: "Subcutaneous administration of an endocrine-mimetic platform allows for prolonged tumor uptake of a tumor targeting protein"
Research Group: Nanobiotechnology
Abstract:
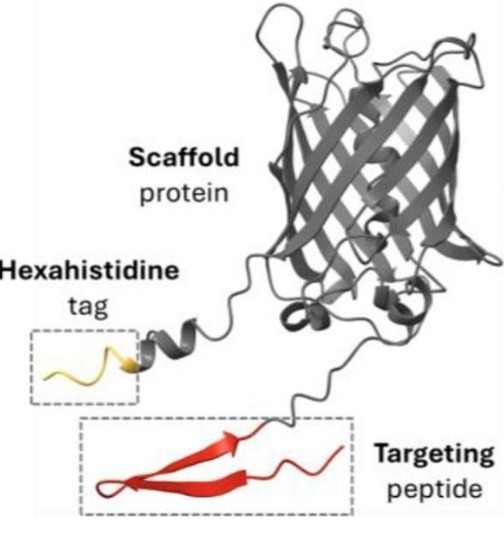
Endocrine-like dynamic protein depots can be fabricated in vitro through the coordination of divalent zinc ions (Zn2+) with solvent-exposed histidine residues on functional proteins, leading to their controlled aggregation. The resulting microparticles, under physiological conditions, undergo progressive disintegration due to spontaneous Zn dilution, enabling a time-sustained release of the protein components. These chemically pure protein-based materials represent promising drug delivery platforms, with demonstrated efficacy in oncology, vaccinology, tissue regeneration, and antibacterial therapies. To enable systemic delivery of the embedded protein, alternative administration routes are potentially suited, but their effectiveness in terms of biodistribution and accumulation in target tissues remains unexplored. Using a CXCR4+ cancer mouse model, we investigated the tumor targeting and permanence of a self-assembling, CXCR4-binding fluorescent protein administered in the form of secretory granules via subcutaneous, intramuscular, or intraperitoneal injection. Our data reveal that subcutaneous administration supports prolonged protein retention at the injection site, its release within the local draining lymphatic vessels, extended circulation time, and significantly higher tumor accumulation 10 days post-injection. Compared to intramuscular and intraperitoneal routes, the subcutaneous pathway presents clear advantages, potentially allowing reduced dosing frequency in protein-based therapies aimed at maintaining steady systemic and target tissue levels.
Article data:
Patricia Álamo, Hèctor López-Laguna, Marianna T.P. Favaro, Alberto Gallardo, Lorena Alba-Castellon, Antonio Villaverde, Ramon Mangues, Esther Vázquez. Subcutaneous administration of an endocrine-mimetic platform allows for prolonged tumor uptake of a tumor targeting protein. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. Volume 690,2026,126585. ISSN 0378-5173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2026.126585.
The UAB, with the Sustainable Development Goals
-
Good health and well-being