New article: "Electrochemical biosensor for early Alzheimer's detection and patient risk stratification using plasma exosomes"
Research group: Biosensing and Bioanalysis
Abstract:
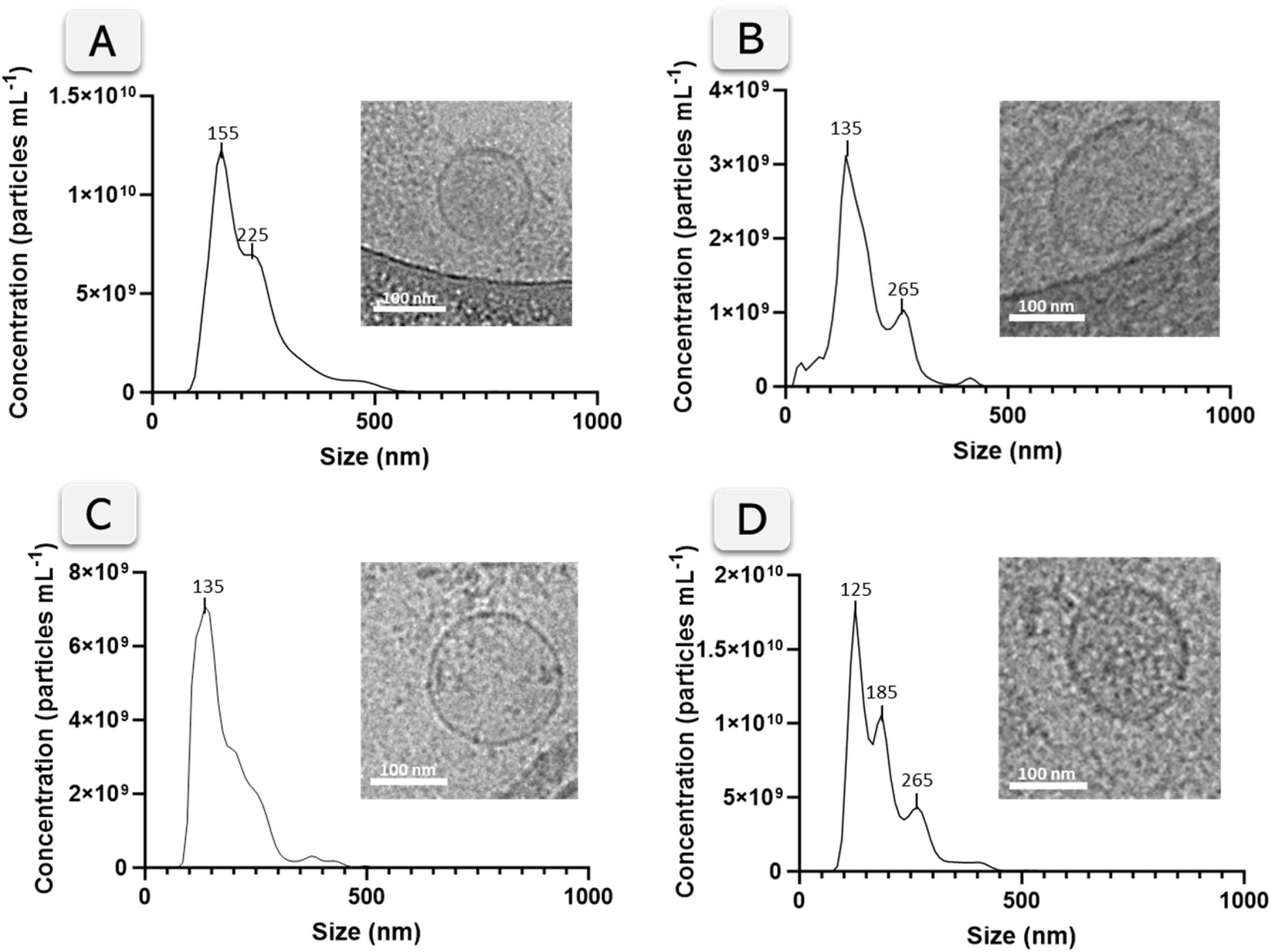
Alzheimer's Disease (AD) is the leading cause of dementia, accounting for 60–70 % of cases worldwide. Early diagnosis remains challenging due to the limitations of current diagnostic tools, which are costly, invasive, and suffer from low patient compliance. Blood-based biomarkers, particularly plasma brain-derived exosomes (BDEs), have emerged as a promising alternative since they carry AD-related molecules and can be isolated non-invasively. In this study, an immunoassay was developed to isolate BDEs using magnetic particles functionalized with an anti-neuroligin-3 (NLGN3) antibody, while the AD-related marker β-secretase (BACE-1) was detected on the captured exosomes. This is the first report combining NLGN3 for for the isolation of BDEs with BACE-1 as a detection target, establishing a novel biomarker panel for AD diagnostics. The assay was evaluated across three readout platforms—optical, chemiluminescent, and electrochemical—with detection limits in the range of 104–105 exosomes μL−1. Among them, the portable electrochemical platform achieved the improved LOD (1.51 × 104 exosomes μL−1, R2 = 0.9829). Plasma samples from patients with AD, mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and healthy controls were analyzed, revealing differences in exosomal BACE-1 levels (p < 0.1, t-test). These findings demonstrate, for the first time, an in vitro diagnostic approach based on a portable electrochemical biosensor for early AD detection in plasma through a novel exosomal biomarker panel. Compared to conventional diagnostics, this biosensor offers a non-invasive and cost-effective solution for AD screening, with the potential to support earlier intervention and patient risk stratification.
Article data:
Rosanna Rossi, Amanda Cano, Arnau Pallarès-Rusiñol, Agustín Ruiz, Merce Martí, Maria Isabel Pividori. Electrochemical biosensor for early Alzheimer's detection and patient risk stratification using plasma exosomes. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. Volume 292,2026,118061,ISSN 0956-5663.
The UAB, with the Sustainable Development Goals
-
Good health and well-being